An Explanation of USB Power Delivery: Functionality of Power Delivery Chargers
- Emily Davis
- Jun 14, 2024
- 5 min read
Numerous methods exist for charging phones and devices, with USB Power Delivery being among the most prevalent.

Numerous Android smartphones available in retail utilize this technology for expedited charging, although Apple has incorporated support for it in a greater number of its devices in recent years. What is USB Power Delivery, and what is its operational mechanism?
USB Power Delivery (USB PD) is a worldwide fast-charging technology applicable to all USB devices. Launched in 2012, it allows devices such as cellphones, computers, tablets, monitors, and docking stations to charge using a single USB cable instead of need a separate power brick.
USB-PD employs the USB-C connector, which has emerged as the ubiquitous wired USB interface. It autonomously identifies the power requirements of the connected device and provides the suitable level while facilitating bidirectional power transfer. You have likely utilized USB-PD numerous times without awareness, particularly as many manufacturers assign proprietary names to fast-charging methods for differentiation (more details are provided below).
What is the significance of USB Power Delivery?
What is the reason for our discussion on USB Power Delivery specifically? Ultimately, an examination of the various fast-charging standards reveals significant rivalry. USB Power Delivery must compete with Qualcomm's Quick Charge, Huawei's SuperCharge, and Oppo's VOOC, among others.
The issue with several charging standards is their proprietary nature. Manufacturers designed them exclusively for their products. A Qualcomm Quick Charge (QC) charger functions effectively with a compatible phone, but it is incompatible with a Huawei handset utilizing SuperCharge.
USB Power Delivery seeks to mitigate this issue via standardization. A USB PD charger can rapidly power your phone and is also compatible with devices from other brands, including larger devices such as laptops. The size of a device, whether diminutive or substantial, and its manufacturer are inconsequential. Utilizing a USB PD charger and cable enables your device to charge at its maximum efficiency, either 24W or 240W.
Prior to USB Power Delivery, the majority of gadgets required a charger or power bank for recharging. A gadget can either take or emit energy, but not simultaneously perform both functions. However, with USB Power Delivery, gadgets now provide reverse charging capabilities. This indicates that there is no necessity to interchange various charger kinds, and you can connect your USB PD devices to other compatible devices.
The video above illustrates numerous instances of the evolution of USB PD during recent years. As manufacturers began to use proprietary fast-charging technologies, each adopted a distinct approach. The output of a charger (W, watts) is calculated by multiplying voltage (V, volts) by current (A, amperes).
Diverse fast-charging standards employ distinct methodologies to enhance production. For instance, Qualcomm elevated voltage to achieve enhanced output (thereby accelerating charging speeds), whereas BBK Electronics, the manufacturer of OnePlus, Oppo, and Realme, employed higher ampere values.
Every approach possesses advantages and disadvantages; nevertheless, the ideal solution would involve integrating gradual adjustments in current and voltage to provide the appropriate power supply for each situation. The USB Consortium, the organization responsible for defining USB specifications, undertook that action. It commenced with USB PD 1.0, which accommodates five, 12, or 20 volts at one, two, three, or five amps.
Explanation of USB PD Power Specifications
USB Power Delivery is available in four distinct versions: 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, and 3.1. The initial version, 1.0, launched in 2012, was quite basic. It provided manufacturers just five distinct profiles for their gadgets, allowing no flexibility in this aspect. The profiles reached a maximum of 100W, as indicated in the table presented during the USB PD 1.0 launch in July 2012.
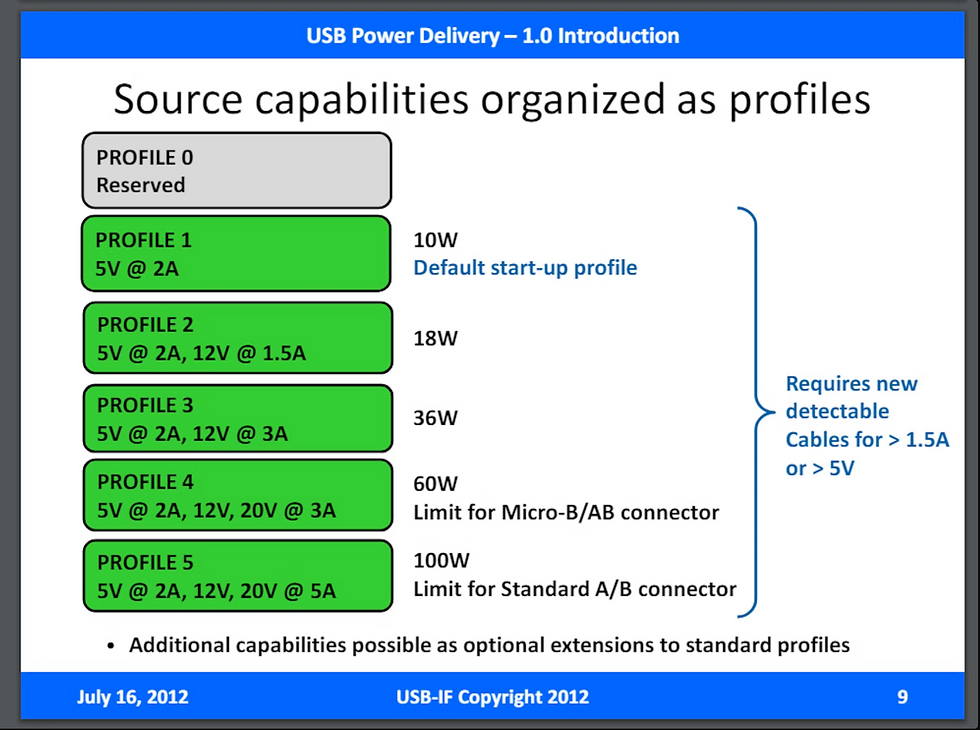
Upon its introduction, USB 2.0 presented more profiles for manufacturers and a variable current according to the device's requirements. It maintained the limit at 100W, sufficient for the majority of applications. The Environmental Coalition on Standards (ECOS) published a table detailing the various levels of USB PD 2.0 and above chargers in their study titled "One Charger to Fit Them All." [PDF]
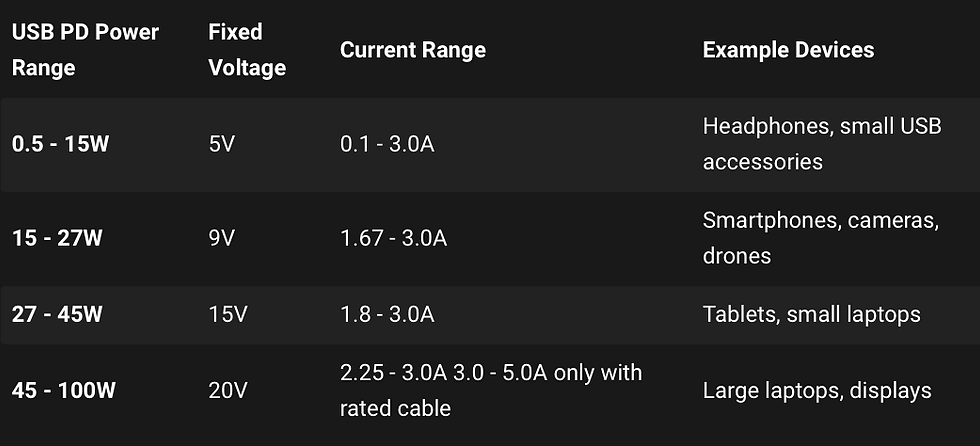
USB 3.0 has identical power profiles to 2.0, although possesses some significant distinctions. The ports with which the cables are compatible will be noticeable during use. USB PD 2.0 is compatible with USB Type A and C ports, whereas 3.0 exclusively utilizes Type C. Nonetheless, the additional advantages of USB PD 3.0 are primarily aimed toward developers, offering enhanced data reporting compared to 2.0. Manufacturers can obtain information such as battery charging rate and device temperature via 3.0 cables.
In 2021, the USB Implementers Forum launched USB PD 3.1. As indicated on its website:
The USB PD Revision 3.1 specification significantly enhances the capability to transmit up to 240W of power using a fully equipped USB Type-C® connection and socket. Before this upgrade, USB Power Delivery was restricted to 100W, utilizing a 20V solution with USB Type-C cables rated for 5A. The USB Type-C specification has been revised to Release 2.1 to provide 240W cable requirements, and with the improved USB PD protocol and power supply definition, this broadens the usefulness of USB power delivery to numerous applications where 100W previously insufficient.
Prior to acquiring a USB PD 3.1 cable, it is important to acknowledge that numerous household chargers will not achieve the 240W output. For example, phone chargers do not require more than 100W, even for rapid charging. Consequently, acquiring a USB PD 3.1 cable will not "unlock" enhanced charging speeds on your phone; if attempted, the cable will conform to the specifications requested by the phone.
What is the procedure for utilizing USB Power Delivery?
What are the initial steps to utilize this technology? To achieve USB PD charging speeds, one requires a charger, a USB-C connection, and a device that is compatible with the standard. Therefore, it is imperative to verify that all items are compatible with USB Power Delivery while shopping.
Consult the manuals and specifications of your devices to ascertain their compatibility with USB PD. It is advisable to investigate your device's compatibility, as certain devices may support USB Power Delivery yet fail to adhere to the USB-C specification.
You may already possess a USB PD-compatible charger. If you possess a USB hub and are curious about the purpose of the "PD" charging ports, they are specialized ports that conform to USB PD regulations. These ports facilitate expedited charging for your USB PD devices.
What Are the Consequences of Utilizing an Incorrect Cable?
The ongoing discourse around proprietary chargers and varying power levels may raise concerns about the compatibility of USB charging cords. Will connecting a OnePlus fast charger to a phone that is incompatible damage the electronics?
Fortunately, as elucidated in the aforementioned video by ThioJoe, the likelihood of utilizing an incorrect cable resulting in gadget explosion is minimal. Countermeasures are in place to prevent a 100W charge from overwhelming a pair of headphones.
ThioJoe could only envision a scenario in which some individual utilized a USB-A to C cable without adequate precautions to regulate the charge. Nevertheless, the cable would need to be poorly constructed for this to occur in a practical context.
However, if you wish to avoid any hazards, it is advisable to utilize a charger specifically built for your smartphone. Provided that you utilize the cable and plug included with your merchandise or acquired from the legitimate store, you should to be concerned. Alternatively, you may select the most reliable USB-C chargers to prevent adverse occurrences.
USB Power Delivery initially appears perplexing and potentially superfluous. Nevertheless, as manufacturers have implemented this standard in their devices, we now possess rapid USB charging that is compatible with most gadgets and allows for bidirectional charging.



Comments